Real-time analytics play a crucial role in various industries, allowing organizations to gain immediate insights and act upon them. However, choosing the best database for real-time analytics can be daunting. This blog post will guide you through the top databases, compare relational and NoSQL databases, and discuss the key factors to consider when selecting the best database for real-time analytics needs.
Analytics Database Summary
- Real-time analytics databases enable businesses to access and analyze data quickly and accurately, considering scalability, speed, data type support & budget constraints.
- Popular real-time analytics databases include Apache Kafka, Singlestore, Snowflake & Amazon Kinesis.
- Use cases for real-time analytics range from observability to fraud prevention & process optimization.
Understanding Real-Time Analytics
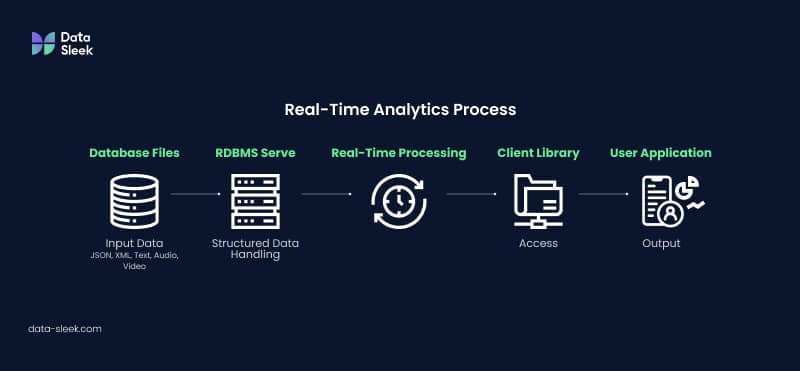
Real-time analytics is the process of gathering, examining, and responding to data immediately, allowing businesses to store data and analyze it in real time. This capability is essential for companies like Netflix and Prime Video, as they rely on real-time databases to deliver seamless user experiences.
But how do you choose the right database for your real-time analytics needs? The essential elements to consider when selecting a database for real-time analytics are scalability, speed, data type support, and budget limitations. These factors apply to both SQL and NoSQL databases, which we will explore further in this post.
Key Factors To Consider For Best Database for Real-Time Analytics

This section will delve deeper into the essential elements mentioned earlier: scalability, speed, data type support, and budget constraints. Each factor is critical in determining the best database for your real-time analytics requirements.
Let’s examine these factors and how they can influence your database selection.
Scalability
Scalability is the ability of a system to manage growing volumes of data and users while maintaining satisfactory performance. A scalable database is essential for businesses that require storing, processing, and analyzing large amounts of data. Scalability can be ensured by incorporating additional resources, optimizing the system architecture, or choosing a database with built-in stream processing capabilities.
Scalable databases offer cost-effectiveness, efficiency, data-driven decision-making, cost reduction, competitiveness, and improved customer experience. Additionally, some databases provide an intuitive web UI for easier management and monitoring, which can further enhance the benefits of a scalable database.
Speed
Speed is essential in real-time analytics, granting businesses access to up-to-date data and swift queries, enabling immediate action and proactive problem-solving. Real-time analytics can enhance business agility, campaign performance, and customer understanding through streaming analytics.
Streaming databases, capable of extracting, transforming, and loading millions of records in seconds, offer accelerated analysis and reduced development time. By opting for a streaming database, whether using a relational database management system (RDBMS) or a NoSQL database, you can effectively manage large volumes of streaming data for real-time analytics.
Data Type Support
Real-time analytics databases support various data types, including semi-structured and modern data formats, without implementing ETL processes. These databases can accommodate structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, such as relational, JSON, XML, text, audio, and video.
Data type support is essential in real-time analytics, facilitating efficient and accurate data analysis. The primary challenge of data type support in real-time analytics is ensuring that the data is stored in a format compatible with the database and that the database can process the data quickly and accurately.
Budget Constraints
Implementing real-time analytics can be costly due to resource restrictions, including computing power, specialized software, and expert personnel. The expense associated with implementing real-time analytics is contingent upon the type of resources required. Budget constraints may include the costs of procuring and sustaining computing power, specialized software, and knowledgeable personnel.
Considering these budget constraints, you can make an informed decision on your organization’s most cost-effective and efficient real-time analytics database.
Are you struggling to keep up with the ever-changing data landscape? Do you wish you could harness the potential of real-time insights to make informed business decisions? Look no further! Data Sleek is here to help.
Top Databases for Real-Time Analytics

Now that we have discussed the key factors to consider when choosing a real-time analytics database let’s explore the top databases in the market: Apache Kafka, Singlestore, Snowflake, and Amazon Kinesis. Each database offers unique features and capabilities that make it suitable for real-time analytics, such as local cache, supports data buffering and streaming data, and is highly scalable.
In the following sections, we will examine each of these databases in greater detail.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a popular NoSQL database that is highly favored for real-time analytics. It’s a document-oriented database that stores data in a semi-structured format, making it highly flexible and adaptable to various data types and structures. This flexibility allows MongoDB to handle large volumes of rapidly changing data, making it ideal for real-time analytics.
MongoDB’s built-in aggregation framework is another feature that enhances its real-time analytics capabilities. This framework allows users to perform complex data processing and manipulation operations directly within the database, eliminating the need to export data for analysis. This results in faster and more efficient real-time analytics.
Moreover, MongoDB supports horizontal scaling through sharding, which distributes data across multiple servers, increasing the database’s capacity to handle large volumes of data. This scalability ensures that MongoDB can maintain high performance even as data volume and user load increase, making it a reliable choice for real-time analytics.
Furthermore, MongoDB’s support for geospatial data types and queries makes it particularly useful for real-time analytics in applications that require location-based data. This includes applications in logistics, delivery services, and IoT, where real-time location data is crucial.
In summary, MongoDB’s flexibility, scalability, and robust feature set make it an excellent choice for real-time analytics, capable of handling large volumes of diverse data and delivering insights in real time.
Singlestore

Singlestore is a cloud-native, distributed, relational SQL database capable of processing transactions and real-time analytics at scale. It is designed to provide the necessary resources to power modern data-intensive applications. Singlestore offers scalability, high performance, and support for various data types.
By utilizing Singlestore, businesses can leverage the benefits of transactions and real-time analytics, allowing them to make informed decisions and enhance their overall performance. It provides scalability, high performance, comprehensive data type support, and cost-effectiveness, making it an attractive choice for businesses requiring real-time analytics capabilities.
Snowflake

Snowflake is a cloud-hosted relational database renowned for its speed and ease of use, with a highly scalable caching layer for optimal enterprise performance.
Snowflake offers a user-friendly experience that enables organizations to make the most of their real-time analytics. However, it is not open source and can be more costly than other databases, so it may not be the best fit for every organization.
Clickhouse Database
Clickhouse has become a strong contender in the real-time data analytics market. Clickhouse Cloud solution has worked hard in providing a managed and scalalable solution.
We recently used them for some real-time operational analytics and we were impressed with their features. We are also Clickhouse Developer certified as we believe this real-time data analytics database will keep growing.
Why Real-Time Analytics Is Essential for Big Data and BI
Real-time analytics has become a cornerstone of big data analytics and modern business intelligence (BI) strategies. As organizations generate massive volumes of data, the ability to run an analytical query and receive insights instantly is critical for timely decision-making. Unlike traditional batch processing, real-time analytics empowers teams to detect trends, respond to events, and optimize operations as they happen—giving businesses a competitive edge in dynamic markets.
- Warehouse and inventory management: Companies implement a real-time and unified pricing and inventory management system, which ensures consistency across central warehouses, store warehouses, and store shelves. The system automatically triggered replenishment or promotions based on real-time stock levels and sales data.
- Order fulfillment and logistics systems today often rely on real-time analytics to break down incoming orders into actionable tasks, assigning them to staff based on factors like location, availability, and workload. These systems also coordinate product movement through distribution channels and optimize delivery routes using live data such as traffic conditions, order volume, and driver proximity—ensuring speed, efficiency, and accuracy in last-mile delivery.
- Fresh supply chain monitoring: Some systems monitored fresh produce in real time using Wi-Fi cameras, temperature sensors, and GPS to ensure product quality and fast delivery.
How To Use Real-Time Analytics to Stop Ransomware Attacks
Ralph Aceves, CEO and Co-Founder of HackerStrike, leverages real-time analytics to combat ransomware and cyber fraud. HackerStrike’s platform detects anomalies indicative of ransomware activity by continuously monitoring device behavior and employing AI-driven analysis. This proactive approach enables the system to identify and block threats before they can encrypt data, effectively preventing attacks in both cloud and on-premise environments. Aceves emphasizes that traditional security measures often fall short against rapidly evolving cyber threats, highlighting the necessity for real-time, intelligent solutions in modern cybersecurity strategies.
Comparing Relational vs. NoSQL Databases for Real-Time Analytics
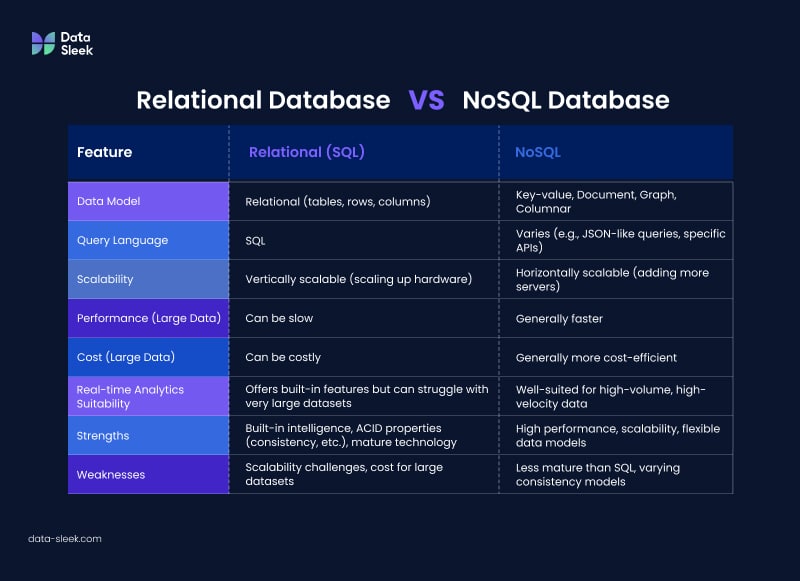
Relational databases, such as PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and Oracle Database, are based on the relational model and utilize Structured Query Language (SQL) to interact with the database. They offer built-in intelligence, scalability, and availability for real-time analytics. However, they can be slow and costly when dealing with extensive data.
On the other hand, NoSQL databases, like DynamoDB and MongoDB, are non-relational databases that employ different data models, including key-value, document, graph, and columnar. They offer in-memory caching, consistent latency, and automatic scaling, making them more suitable for handling large volumes of data quickly and cost-efficiently.
In conclusion, both relational and NoSQL databases have their pros and cons when it comes to real-time analytics. The choice between the two depends on your organization’s specific needs, such as the types of data being processed, the required speed of analysis, and the budget constraints. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each database type, you can make an informed decision that best suits your real-time analytics requirements.
Integrating Real-Time Analytics with Existing Infrastructure
Real-time data integration refers to immediately processing and transferring data upon its collection, which can be accomplished through technologies such as change data capture (CDC) and transform-in-flight. These technologies enable organizations to enhance the accuracy, expedite decision-making, and improve the customer experience by providing immediate insights into customer data and transactions.
However, real-time data integration presents challenges such as latency, quality, and scalability. By understanding and addressing these challenges, businesses can successfully integrate real-time analytics with their existing infrastructure and harness the power of real-time data.
Use Cases for Real-Time Analytics Databases
Real-time analytics databases are utilized in multiple industries, including e-commerce, finance, healthcare, and IoT. These databases offer various use cases, such as observability, user behavior, security and fraud analytics, IoT and telemetry, personalization and experience, fraud and error prevention, process optimization, preventive maintenance, regulatory compliance, credit scoring, financial trading, and detecting and blocking fraudulent transactions. Organizations across different industries can gain valuable insights, streamline their processes, and enhance their decision-making abilities by employing real-time analytics databases.
For example, real-time analytics can help with regulatory compliance in the finance industry by providing immediate insights into customer data and transactions. It can also assist with credit scoring by providing instantaneous insights into customer creditworthiness, financial trading by providing direct insights into market trends and prices and detecting and blocking fraudulent transactions by providing immediate insights into suspicious activity.
By managing data and leveraging real-time analytics databases, businesses can address various challenges and capitalize on opportunities in their respective industries.
Summary
In conclusion, real-time analytics databases are critical in various industries, allowing businesses to gain immediate insights and make informed decisions. Choosing the correct database for real-time analytics can be challenging. Still, by considering the critical factors of scalability, speed, data type support, and budget constraints, you can make an informed decision that best fits your organization’s needs. This blog post has provided an overview of the top analytics databases for real-time analytics, including Apache Kafka, Singlestore, Snowflake, and Amazon Kinesis, as well as a comparison between relational and NoSQL databases. With this knowledge, you are better equipped to select the most suitable database for your real-time analytics requirements and capitalize on real-time data opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which database is used for real-time applications?
Singlestore Database is the best option for real-time applications as it offers many features that allow scalability and high data availability across multiple databases. With its Real Application Clustering, Oracle Database provides a reliable and secure environment to run critical applications.

What is the most widely used database for real-time analytics?
MongoDB used to be a great choice, but querying large data sets for real-time analytics is not ideal. We usually recommend Singlestore, a database built for real-time analytics and AI. Check out our data challenges section under our data architecture consulting services, and don’t hesitate to contact us if you have questions.
Is SQL good for real-time data?
SQL is well-suited for real-time data analysis due to its efficient query language and wide acceptance among enterprise developers.
Which database engine is ideal for real-time analytics in memory?
Redis is great for real-time analytics in memory, as it boasts a highly scalable caching layer that ensures optimal performance and AI-based transaction scoring that simplifies fraud detection. However, Singlestore supports a memory engine and SQL and MySQL protocols, making it a more accessible solution.
What is database analytics?
Database analytics is managing, analyzing, and extracting insights from database data. It uses analytical tools and techniques to understand trends and relationships among large datasets. Organizations can gain valuable insights and make better decisions by leveraging database analytics.



