The concept of Unified Data Management (UDM) has gained increasing significance over the past couple of years as businesses collect and generate vast amounts of data during their daily operations. Managing all this data, especially as it comes from unstructured repositories and IoT devices, presents a significant challenge. Historically, many organizations developed their software systems on an ad-hoc basis, comprising a range of different programs and data management techniques.
These systems and management techniques evolved as businesses and organizations grew and expanded. Without a clear data strategy and unified data management, the organization’s internal departments began developing their internal systems and methodologies for collecting, storing, processing, and analyzing data.
This approach resulted in a disparate structure with duplicate, inaccurate, or incompatible data and tools that serve an identical purpose, leading to the formation of siloed systems and siloed data across different teams. Organizations embarking on UDM initiatives should first understand why data strategy must precede data management to ensure consolidation efforts are strategically aligned and avoid recreating the silos they set out to eliminate.
Using tools with identical capabilities leads to inefficiencies and increased costs. Siloed systems and redundant tools hinder the achievement of business goals by making it difficult to access, integrate, and utilize data effectively. In the digital age, lacking accurate and adequate business data results in a loss of business insight and trend analysis, a reduction in operational efficiency, and increased business costs.
The solution to these issues lies in Unified Data Management (UDM). This process consolidates disparate data from various sources to create a single, unified dataset within a data warehouse. Doing so provides access to comprehensive, consistent data across the entire organization, fosters interdepartmental cooperation, and enables better regulatory compliance. Unified data management optimizes data workflows and end-to-end operations by reducing time and resource waste, resulting in significant cost savings.
However, the most significant benefit granted by UDM is the ability to derive better business insights, which promotes further growth and expansion. Aligning unified data management initiatives with business goals ensures that data strategies directly support organizational objectives and drive measurable value.
Unified data management requires strategic alignment across the organization. Our data strategy consulting team can help you build a cohesive data foundation.
What is Unified Data Management
As previously explained, Unified Data Management is a strategic process that consolidates a range of disparate data sources into a single, unified data source stored within a data warehouse. This process is accomplished by identifying integration factors within the existing data and data sources, transforming and storing said data in a common data repository within a data warehouse.
The data warehouse can be likened to a data center, acting as the heart of the organization where all incoming data is processed, cleaned, and optimized before being distributed to various departments.
After the data is cleaned, consolidated, and stored, it is integrated throughout the entire system into a single framework that supports complete data optimization. Furthermore, UDM also provides a common space for cleaning, parsing, and transformation of the data, which is applied uniformly across all data in the data warehouse to standardize it throughout the organization.
With that said, it’s essential to understand that unified data management isn’t a universal toolset that all businesses and organizations can use out of the box. Instead, it’s a comprehensive data architecture that relies on a coordinated range of tools and technologies from different disciplines, including data governance, master data management, data integration, data quality, and business intelligence. A modern UDM architecture often incorporates a data fabric, which uses data virtualization and other technologies to deliver a unified, organization-wide view of data, regardless of its location or format.
For UDM to be successful, its components must be seamlessly integrated through a standard interface or platform, enabling centralized administration, monitoring, and iterative development. A unified platform and unified system play a critical role by consolidating security, user management, and auditing functions into a single, cohesive environment, improving security, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Key Aspects of Unified Data Management:
- Centralized data consolidation and storage
- Standardized data cleaning and transformation
- Seamless integration of multiple data sources
- Real-time data access and sharing
- Enhanced data governance and compliance
- Creation of a single data narrative that promotes consistent insights across departments
Unified data management acts as a centralized platform that centralizes data from multiple sources into a single, easily accessible location. This approach enhances reporting and analysis accuracy by increasing visibility across locations, enables real-time decision making by providing the most up-to-date information, and allows organizations to gain real-time insights, discover new opportunities, and make fully-optimized decisions.
Data Management vs Unified Data Management
People often use “data management” as a catch-all term when speaking about data because they believe that data management and unified data management are interchangeable. They aren’t.
The truth is that data management and unified data management are closely related concepts, but they’re not the same thing. Data Management is the umbrella discipline that encompasses all the policies, processes, tools, and practices necessary to collect, store, secure, govern, and utilize data effectively throughout an organization. Managing various data types and large data volumes is essential, as organizations must handle diverse information streams and the exponential growth of data.
The core functions of Data Management include:
- Data Collection
- Data Architecture and Modeling
- Data Governance
- Data Lifecycle and storage management
- Data Quality Management
- Data Security and Privacy
- Master Data management
- Metadata Management
On the other hand, Unified Data Management is a distinct procedural approach to data management that focuses on breaking down data silos by integrating data from disparate sources into a single, cohesive view. The ultimate goal of Unified Data Management is to enable end-to-end visibility and alignment across an organization by integrating all accessible data. UDM integrates multiple tools to handle data from diverse sources and formats, making it possible to process and govern large data volumes efficiently.

Key Aspects:
- Creates a single source of truth.
- Enables cross-functional access and analytics.
- Often combines real-time and batch data processing.
- Unifies data across systems (CRM, ERP, marketing, finance, etc.).
- Supports holistic dashboards and strategic insights.
Think of Data Management as an entire restaurant—with everything from ingredients (data sources) and utensils (ETL, warehouses) to hygiene standards (stewardship, governance and quality). Unified Data Management is like the meal prep area—where everything is brought together and organized to create clear, attractive, and actionable outcomes (business insights) before being delivered to customers.
Why Fragmented Data Fails Modern Businesses
Fragmented data scattered across disparate systems and disparate tools leads to operational inefficiencies, errors, and missed opportunities because it prevents businesses from achieving a holistic view of their operations and hinders data-driven decision-making. Disparate tools also hinder efficient access to data, making it difficult for teams to retrieve and use information quickly and securely. This challenge is especially pronounced in construction, where Procore, BIM platforms, and accounting systems often create construction data silos that delays reporting and erodes margins.
Messy, duplicated, and fragmented data has evolved from a minor inconvenience to a full-blown crisis that affects organizations across different industries. It also overwhelms entire IT departments, forcing them into a reactive maintenance mode as they attempt to troubleshoot various issues caused by poor data management.

Fragmented data is filled with inconsistencies and errors, which often forces manual reconciliation and data entry. These typically consume valuable time and resources that a company could otherwise allocate to more strategic initiatives.
A clear illustration of this occurs in the construction sector; construction companies experience this acutely when project data is scattered across BuilderTrend, QuickBooks, and Excel spreadsheets. A construction data warehouse eliminates these inconsistencies by creating a single source of truth for cost, schedule, and field data.
However, resource waste isn’t the only issue caused by fragmented data; inconsistencies and errors also lead to delays, missed deadlines, and reduced overall productivity. For construction firms, these costs manifest as margin erosion, cost overruns, and delayed project delivery. See how builders calculate the ROI of consolidating fragmented construction data into a single source of truth. It also hinders decision-makers who, lacking a single source of truth, can’t make informed business decisions. These wasted resources have massive repercussions on a business.
Fragmented data and the use of disparate tools increase security risks by complicating access control and creating more vulnerabilities for unauthorized access. In such environments, it becomes challenging to review data for compliance and governance, as tracking changes and ensuring regulatory adherence is more difficult. Not to mention that relying on disparate systems creates multiple entry points for attackers, leading to data breaches and lengthy legal disputes over loss of data.
Combining centralized access control with unified data management offers a more efficient way to manage user permissions and data access, enhancing oversight while minimizing security risks.
Unified Data Management as a Strategic Asset
Since fragmented data has very adverse effects on the organization’s operational efficiency and, ultimately, profitability, unified data management has become crucial for all organizations that leverage data as their strategic asset.
By consolidating and standardizing data and tools across an entire organization, UDM provides a holistic view, which facilitates actionable insights derived from the data and supports strategic initiatives down the line, as well as a range of benefits that positively impact operational efficiency and profitability.
For transportation and logistics companies, this means building a unified transportation data infrastructure that powers real-time operational decisions. Data unification breaks down data silos, enabling collaboration and integration among different teams, and supports the modernization of data architecture for better decision-making and business growth.
Investing in UDM leads to a reduction in time spent handling data, faster time-to-insight for analytics, reduced data duplication and waste, lower compliance and governance risks, and improved customer experiences. UDM also provides enhanced visibility across the organization, supporting better reporting, analysis, and data governance. It supports data migration and preparedness, allowing both technical and business users to communicate and act on data insights. Unified data management simplifies data compliance through streamlined security and consistent governance, making it easier to meet international regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Additionally, UDM enhances data quality by profiling, cleaning, and standardizing data, ensuring accuracy and consistency. Real-time decision making is enabled by the ability to gather, process, and output data quickly from multiple sources. UDM also empowers effective marketing campaigns by providing integrated, high-quality data for precise targeting and improved campaign performance.
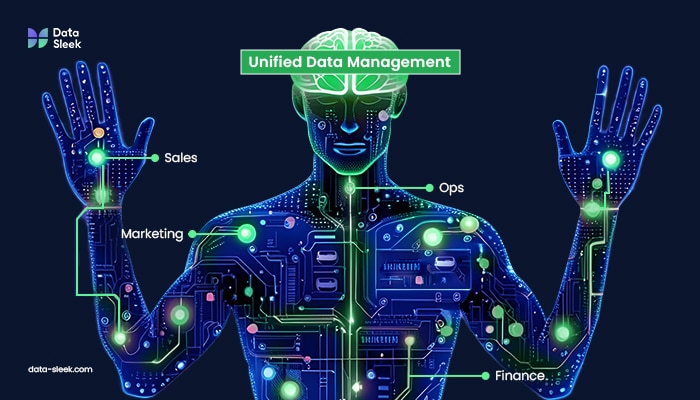
Think of your organization as a body and UDM as its brain. Each department (or limb or organ) can work independently, but ideally, they should function as part of the whole. Without the brain, the arms don’t know what the legs are doing, and the heart might race while the lungs slow down. Communication between departments breaks down, leading to decision-making delays and impaired performance.
Unified Data Management is that brain. It collects data from every part of the organization, interprets it, and sends clear, real-time instructions that keep the body, or in this case, an organization, well-coordinated and responsive, with enhanced visibility and the ability to output data for real-time decision making.
Managing Data Architecture for Unified Data
A robust data architecture is the foundation of any successful unified data management system. Managing data architecture means designing and implementing a framework that can seamlessly integrate disparate data sources, ensuring that all business data is accessible, consistent, and reliable. By adopting a unified data management system, organizations can eliminate data silos and create a single, cohesive view of their data, which is essential for maintaining data integrity, enforcing data governance, and upholding data quality standards.
A unified data platform plays a pivotal role in this process by providing a centralized data repository where all data sources converge. With features like data virtualization and advanced data integration, organizations can efficiently access and combine data from multiple systems without the need for complex migrations. This centralized approach not only streamlines data management processes but also enhances operational efficiency by making up-to-date information readily available for analysis and decision-making.
Ultimately, a well-managed data architecture empowers organizations to break down barriers between departments, improve data access, and establish a single source of truth. This enables informed decisions, supports strategic business objectives, and drives business growth in an increasingly data-driven world.
How To Implement Unified Data Management
UDM is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and many of its aspects will depend on your organization’s current data architecture and business needs. However, almost all UDM implementations share the following steps:
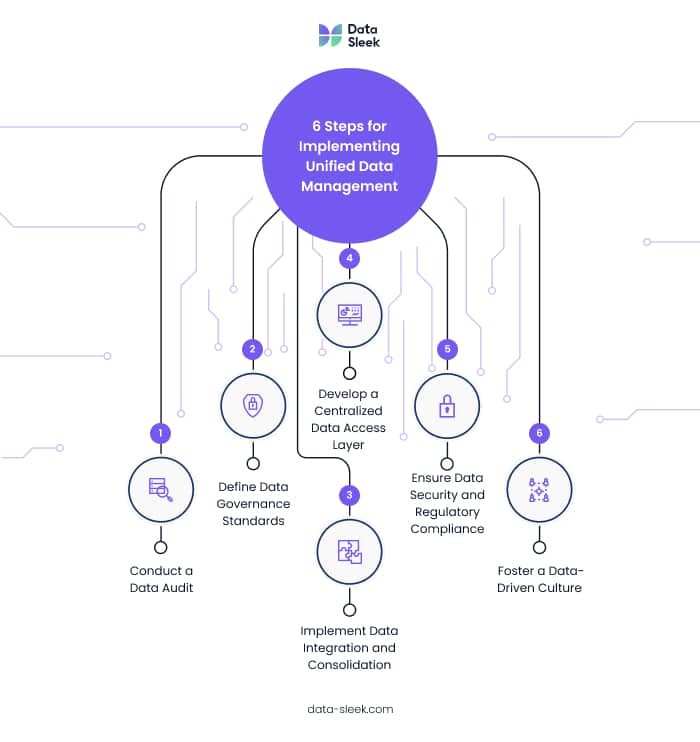
Step 1: Conduct a Data Audit
The first step towards implementing unified data management is to assess the data, tools, and architecture you already have. Data audits will allow you to identify the data, its sources, structure, and ownership, ensuring that you’re not unifying irrelevant, obsolete, or redundant data.
Step 2: Define Data Governance Standards
Well-defined data governance standards outline all the systems, tools, and data repositories, as well as how they will connect and interact with one another. With this in place, you’re running the risk of creating more data silos and shadow IT practices. Governance also sets rules, and without them, you’re risking non-compliance, data leaks, and making decisions on inaccurate data.
Step 3: Implement Data Integration and Consolidation
Raw data is rarely productive to use across an organization. Still, integration and consolidation take raw data from disparate systems, remove inconsistencies, duplicates, and errors, and leave you with high-quality data stored in your data warehouses, thus eliminating data silos and leading to enhanced operational efficiencies.
Step 4: Develop a Centralized Data Access Layer
Centralized data is only valuable if those who need it can use it, which is why it’s essential to implement a centralized data access layer (usually a shared interface or dashboard). Developing a centralized data access layer will reduce dependencies on technical teams and foster a data-driven culture while also driving cross-functional and cross-departmental collaboration.
Step 5: Ensure Data Security and Regulatory Compliance
Without adequate data security and regulatory compliance measures in place, unified data magnifies the impact of breaches and non-compliance. It’s like taking everything valuable and putting it in one place for attackers to grab. Ensuring data security and regulatory compliance through ongoing audits and real-time monitoring of your systems ensures that said systems are resilient to attacks and compliant with regulations.
Step 6: Foster a Data-Driven Culture
Though UDM may seem revolutionary from the perspective of an organization that relied so long on fragmented data, the technology alone won’t transform your organization—people will. It is imperative to cultivate a data-driven culture, as it will further encourage and streamline the adoption of UDM.
Data Quality and Cleansing in Unified Data Management
Ensuring high data quality is a cornerstone of effective unified data management. Without reliable, accurate, and consistent data, organizations risk making decisions based on flawed information, which can undermine operational efficiency and business performance. Data cleansing is the process of identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies, and redundancies within the data, transforming raw information into a trustworthy asset.
A unified data management system streamlines data quality initiatives by offering robust data validation, normalization, and standardization tools. These capabilities help organizations detect and resolve data issues at scale, ensuring that unified data is both accurate and ready for analysis. By prioritizing data cleansing as part of their data management strategy, businesses can eliminate the risks associated with poor data quality and unlock the full potential of their data assets.
Reliable, high-quality data not only supports better decision-making but also enhances operational efficiency, reduces compliance risks, and enables organizations to respond quickly to changing business needs.
Creating Effective Data Models for Business Insights
Transforming unified data into actionable business insights starts with creating effective data models. A data model visually represents the structure, relationships, and rules governing an organization’s data, providing clarity and context for analysis. Well-designed data models help organizations understand their unified data, minimize data inconsistencies, and ensure a single source of truth across the enterprise.
A unified data platform offers powerful data modeling tools, data governance processes, and visualization capabilities that enable organizations to design data models tailored to their unique business requirements. These tools facilitate the creation of models that not only improve data quality but also support advanced analytics and reporting.
By leveraging effective data models, organizations can uncover patterns, identify trends, and generate actionable insights that drive strategic business objectives. This approach ensures that every decision is informed by accurate, up-to-date information, maximizing the value of unified data.
Leveraging Data Platforms and Tools
To fully realize the benefits of unified data management, organizations must leverage modern data platforms and tools. A unified data platform serves as a centralized hub for all company data, integrating structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from multiple sources. This unified approach breaks down data silos, enhances data access, and provides a comprehensive view of the organization’s information landscape.
Data management tools—such as those for data integration, data quality, and data visualization—are essential for processing, analyzing, and presenting unified data. By utilizing these tools within a unified data platform, organizations can streamline data management processes, improve data quality, and generate valuable business insights.
The result is greater operational efficiency, reduced costs, and the ability to make informed, data-based decisions that support business growth. By embracing the right data platforms and tools, organizations can transform their data infrastructure into a strategic asset that drives innovation and competitive advantage.
Common Challenges When Unifying Disparate Data
While it seeks to eliminate, overcome, or at least alleviate the challenges associated with fragmented data and disparate systems, Unified Data Management isn’t without challenges of its own. Here are some of the most common challenges organizations face when unifying disparate data:

- Inconsistent Data Formats—Different departments often store data in different formats, which makes integration more difficult.
- Data Silos—Numerous teams store their data in isolated systems without cross-access. These silos are the antithesis of a unified data view, often resulting in duplication and inefficiencies.
- Poor Data Quality—Dirty data, including duplicates, outdated data, or incomplete entries, must be cleaned before data consolidation and integration. Otherwise, wrong or dirty data can compromise the entire system.
- Lack of Metadata and Context—Without explicit metadata (which is the data about the data), it’s hard to understand the origin and relevance of data, as well as its interactions with other data sets. This lack of distinct metadata leads to misinterpretation.
- Integration Complexity—Integrating legacy systems, modern cloud platforms, and third-party APIs often requires extensive customization and coordination, demanding a flexible integration strategy. Managing large data volumes during integration adds another layer of complexity, as organizations must handle the exponential growth of data generated by modern enterprises.
- Data Ownership, Compliance, and Security—Lack of data ownership also implies a lack of management, leading to conflicting practices. This is particularly true when it comes to sensitive data, which has to comply with regulations.
- Resistance to Change—Teams and departments that rely on disparate systems are often accustomed to working in such environments and may resist transitioning to a unified model. This unproductive mindset is why cultivating a data-driven culture is key.
United data management helps address these challenges by consolidating output data from multiple sources—such as weather feeds, maps, and lab reports—into a single, cohesive system. This approach not only streamlines collaboration across departments but also improves data quality and enables unified data insights for better business intelligence and scalability.
Unlock the Strategic Power of Unified Data
Pursuing a unified data model is critical for any modern business or organization that wants data-based decision-making, and unified data management provides just that—a unified view of data that reduces operational inefficiencies and enhances data-driven decision-making.

If you want to integrate unified data solutions and transform your business, contact us today, and we’ll help you turn your data into a strategic asset that drives efficiency and innovation. Visit our website and schedule a free consultation with our data expert today.


