If you’ve ever shown up on time for your doctor’s appointment just to be handed a clipboard with a stack of pages on it thicker than a doctoral thesis and wondered, “how is handing over all of my personal information going to help me feel better?”, you’re in good company. Nearly all of us have been there in the waiting room, filling out endless forms about our health history, financial information, and insurance provider.
In the information-saturated world we live in, big data is a critical component of the healthcare industry. Healthcare Data management is the backbone for many advancements and improvements in patient care, medical research, and healthcare management.
The landscape of modern medicine has undergone a significant transformation in recent years. Patients want to know that when they seek medical care, whether preventative or remedial, they can find the help they need, but that isn’t always the case. Concerns about the quality, accessibility, and availability of medical care have become more acute in the last few years.

The Onset Symptoms Of A Digital Shift
The COVID-19 pandemic brought to light a widening gap in healthcare equity, and healthcare organizations are more keenly aware than ever that health data, and healthcare data management are taking center stage in providing high-quality healthcare to as many as possible.
But even with the best of intentions, challenges persist. Case in point: more than 80 percent of counties in the United States contain “healthcare deserts,” lacking access to adequate healthcare infrastructure. It isn’t just a lack of emergency medicine, either. Pharmacies, primary and trauma care, and affordable options like urgent care and walk-in clinics are inaccessible to millions.

The Role of Digitization in Expanding Access to Care
Considering that 12.4 percent of the US population lived below the poverty line in 2022, an increase of nearly 5 percent from 2021, it’s not financially feasible for millions of individuals to travel long distances for expensive healthcare options.
But take heart. Discouraging as this may sound, the prognosis is brighter than it seems. Using healthcare data management systems helps healthcare organizations create a comprehensive view of patients, households, and patient groups—composite profiles that provide status and enable predictions. What does this mean for patient outcomes?
The world of high-quality, comprehensive healthcare no longer requires visits to many facilities and taxes far fewer resources. Digitization of healthcare records allows all healthcare industry sectors to coordinate care and work symbiotically with patients, insurance companies, and care facilities.

The Data Prescription: Improved Outcomes
Healthcare is a fast-paced world, and as technology becomes the epicenter of our world, data has become a critical healthcare asset, driving innovation, improving patient outcomes, and optimizing operational efficiencies. Clinical decision support systems play a crucial role in enhancing healthcare data management by analyzing evidence-based data within various care settings, thereby supporting healthcare providers in delivering improved treatment results and personalized care.
From electronic health records (EHRs) to advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI), data is reshaping how healthcare is delivered and experienced. While electronic health records (EHRs) are widely used, electronic medical records (EMRs) are also integral to health data management systems, particularly in hospitals where they help organize, integrate, and analyze health data to improve patient care outcomes. However, as promising as it sounds, the integration and utilization of data in healthcare come with a unique set of challenges that data management systems are able to address to harness its potential fully.
Healthcare’s Data Deluge
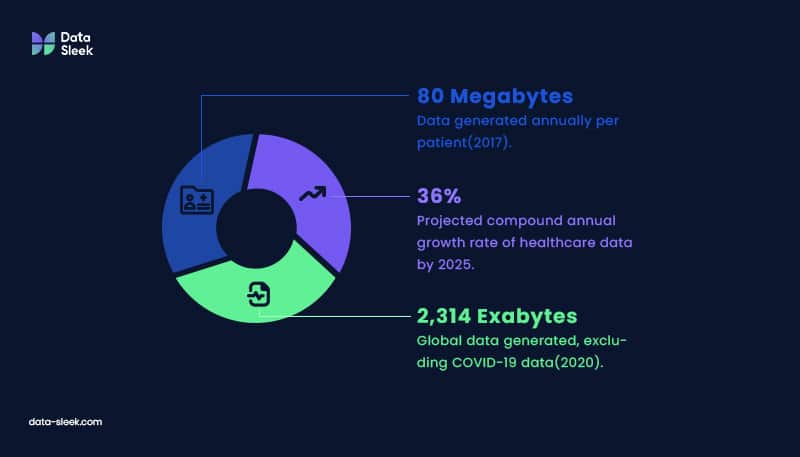
The integrative approach to medical data comes not a moment too soon. According to 2017 estimates, a single patient generates nearly 80 megabytes of data each year in imaging and other medical record data. The data growth rate within the healthcare industry is far faster than what’s projected for other major industries, including manufacturing, financial services, and media and entertainment.
And that volume of data shows no sign of slowing: data forecasters predict that by 2025, the compound annual growth rate of data for healthcare will reach 36%.
The quantity of healthcare data generated is so massive that it can be helpful to think of it in planetary terms. One study estimated that as many as 2,314 exabytes of new data were generated worldwide in 2020. If we imagine one gigabyte as the size of Earth, then a single exabyte would be the sun. And that 2,314 exabyte estimate didn’t even include COVID-19 data. So how does the healthcare industry keep from being sucked into a data black hole?
Electronic Health Records to the Rescue
A 2014 federal mandate required all private and public healthcare providers to adopt EHRs to recruit, store, and use patient data. An elegant transition from handwritten medical notes, EHRs are digital versions of patient records stored on a computer and maintained by the healthcare provider. Healthcare organizations synchronizing with each other to communicate and store data on a single platform means a larger individual medical record for each person. Electronic health records help compress, distill, and filter patient information within healthcare organizations, not just between them. All patient information can now be accessed via patient portals.
Most mid-sized hospitals have the capacity to perform all kinds of diagnostic imaging, including CAT scans, X-rays, and MRI scans. The resulting medical records used to rely on disorganized paper-based healthcare data management. With electronic health records (EHRs), healthcare organizations save resources by storing and transmitting medical data electronically. EHRs turn unstructured data into high-accuracy healthcare data.
Giving more people accessibility to medical professionals and bringing down costs of care means more resources are left to customize patient care.
A Personalized Prescription from a Clinical Data Management Consultant
Customizable medicine is one of the highest predictors of good health prognoses, and arguably, the most promising application of data in healthcare is precision medicine. By analyzing genetic data, lifestyle factors, and environmental influences, healthcare providers can tailor treatments to individual patients. However, the integration of various types of data for personalized care poses significant challenges due to unstructured data. This approach increases the efficacy of treatments and minimizes side effects, as therapies are customized to the patient’s unique biological makeup.
The advent of affordable wearable devices means ending the one-size-fits-all approach that has dominated the field for decades. As a result, patients are receiving more personalized care, leading to improved outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system. Common devices like blood pressure cuffs, weight scales, and glucose readers have reinvented risk identification in healthcare. Even a patient’s smartphone can provide insights into an individual’s health, seamlessly integrating into daily routines.

Data-driven predictive models can forecast patient outcomes, enabling early intervention and preventing complications. For example, algorithms can analyze EHRs to identify patients at risk of developing chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease, allowing for proactive management. Electronic health records
Dangerous Data Vulnerabilities and Data Security
The digitization of all of this information opens up never-before-seen possibilities for medical care, but it can also present health data management challenges with patient safety, data security, and data quality.
The quantity of data, combined with the coordination between healthcare facilities, can lead to issues with interoperability. Healthcare data is often trapped in siloed systems, such as different EHR platforms, laboratory information systems, and imaging systems. These systems may not communicate effectively with one another, making it challenging to integrate data and gain a comprehensive view of a patient’s health.
The lack of standardized data formats and coding systems across healthcare providers further complicates interoperability, especially for data analysis. These different systems act as different languages, and without a translation tool, they turn healthcare data into a Tower of Babel. One hospital may use ICD-10 codes for diagnoses, while another uses SNOMED CT. Healthcare data management resources like Data-Sleek can improve communication and eliminate data silos that prevent seamless operability.
Bringing Healthcare Data Management to Our Homes
Jabra Enhance, a healthcare tech company familiar with the importance of clear communication, has made it its mission to deliver high-quality, advanced audio-augmentation tools to the hearing-impaired community without users ever having to leave their homes. As word got out and their customer base grew, a data deluge disrupted their data infrastructure.
Faced with non-unified data from multiple sources, their data became siloed and fragmented. Their operability issue was that Jabra Enhance was now the custodian of customers’ sensitive personal health information (PHI), meaning that data security and HIPAA compliance were an immediate priority.
Using pipelines and a cloud-based data platform, Data-Sleek provided data security, ensured regulatory compliance, and enabled self-service data analytics. With the help of Data-Sleek’s data management architecture and some data scientists, Jabra Enhance scaled its growth at triple-digit rates and delivered the transformative power of communication to the world safely and conveniently.
Health Data Management and Patient Security
Hackers and cybercriminals highly seek personal health information stored in clinical data management systems. Health data management systems without secure data encryption open the door for breaches. This information is rife with sensitive personal medical information such as diagnoses, lab results, and treatment information, but the most insidious privacy incursions avail themselves of patient PHI for the demographic and clinical information, notes, billing information, and identification and insurance claims.
Given the volume of sensitive information found in electronic health records and the rapidly multiplying amount of data, the healthcare industry is uniquely ill-equipped to protect it. The threshold to gain access to healthcare data is far lower than it is in other industries. According to a report by the IDC, investments in security and privacy protections in the healthcare industry are among the lowest of all industries.
To illustrate, in 2016, there were 3 million consumer credit card complaints, 42% of which were related to fraud and 13% connected to identity theft. Victimizing nearly 1% of the U.S. population during the year, these cases are no trivial matter, to be sure.
The Threat of Cybercrime In Healthcare
But what of the threat to our health records? The theft and sale of patient data on “dark web” stores look not much different from an Amazon marketplace. In fact, nine times more medical than financial records were breached in 2016. We’re talking about 27 million people who had their healthcare data stolen, sold, or otherwise compromised. When nearly 10% of the U.S. population is affected, it’s time to figure out the solution.
This lack of healthcare data management and data security means data management systems have difficulty catching up with data management challenges. Constantly trying to close the gap in critical data management leads to even less investment in advanced architectures, edge computing, robotics, and other necessary technologies.
Medical records aren’t only exposed to cybercriminals trying to make money on the black market or extort large sums from healthcare organizations and insurance companies. Trusted healthcare providers can also access patient records and misuse them for personal gain, and this happens with staggering frequency.
Insider Threats and Data Security Measures
One report found that healthcare insiders were responsible for 20% of all breaches in 2020. The finding underscores that as healthcare organizations amass greater and greater quantities of sensitive, highly sought-after patient data, the assorted threats to keeping it private are growing in lock-step.
Evidence like this underscores a key takeaway here: as healthcare organizations accrue greater quantities of valuable, highly coveted electronic health records, the faster health data management systems have to work to mitigate the threats. Hospitals using healthcare data management systems keep their electronic medical records encrypted and out of reach.
Using Data Analytics For Population Health Management
The goal of health information management comes down to one empirical metric: improved patient outcomes. A potent tool built into health data management systems is population health analytics. PHA uses big data to analyze health trends across large populations, helping to identify public health risks, track disease outbreaks, and inform policy decisions.
Health information management can parse health data by stratifying it based on germane social factors, adding to its valuation. Social determinants of health, like income, education, and environment, are pertinent components of individual health outcomes. Health data management allows practitioners to better understand and address health disparities.
Decoding Data Diligence
A significant but common puzzle that healthcare organizations face is ensuring that their clinical data management systems comply with vacillating and complex data governance regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, which governs the protection of patient data.
Data governance regulations have the distinct difficulty of being capricious, rigid, and highly punitive, so ensuring compliance while maintaining data accessibility for legitimate purposes is a delicate balance. However, healthcare providers cannot afford to miss the mark; the average cost of a breach for a healthcare organization is about $8 million, and the estimated costs of a total breach cost can exceed $400 per patient record exposed.
The Shift Toward Prevention and Digital Tools
Thanks to the affordability of health trends like wearable medical devices, the volume and velocity of information healthcare organizations receive are larger than ever. Once disease treatment was prioritized, healthcare was primarily focused on disease prevention.
The natural progression is toward the adoption of various digital tools—health data management systems, machine learning, data encryption, and data analytics. The new “smart” healthcare facility uses clinical data management systems to ensure the best possible health outcomes. They are the gold standard for storing data, keeping relevant data organized, and coalescing fragmented data from various sources.
The Growing Value of Integrated Data Management
The utility of healthcare data management systems is no fleeting health trend. Hospitals are using data integration tools to merge medical images, insurance claims, health records, and claims data into one database, like cloud platforms, and this is on the rise. Hospitals that have invested in this kind of data infrastructure were responsible for $57.53 billion of the U.S. healthcare economy in 2023. That number is expected to reach $187.20 billion. Statista figures also prove this exponential growth—from $35.9 billion in 2021 to an impressive $83 billion in 2026.
What the Doctor Ordered: The Data Directive

With cutting-edge technologies continuously introduced, the healthcare industry’s data boom will only continue. Patient security and protection, epidemiological tracking, AI diagnostics, and EHR storage all rely on turning data into meaningful medical outcomes. So, what can healthcare organizations do to ensure their patient protocols remain current?
The Role of Data Management Systems and Training
Putting the data architecture in place: Using a data management system is a top priority. Healthcare data management systems work tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure facilities don’t jeopardize their regulatory compliance, keep PHI secure, and so much more.
Training the hands that heal: Even the best tech in the world can’t protect data if the humans using it aren’t up to speed. Investing in training. Make sure that healthcare staff can recognize phishing emails and all personnel know the latest security protocols.
More than ever, data is of the essence in the healthcare industry. Safe, relevant, structured data is the key to staying on top of protocols and ensuring a safe, healthy, and healthcare future. Data-Sleek has the tools, services and experience to let data do its most important job: saving lives.
Is It Time To See A Specialist?
Ready to transform your healthcare organization with smarter data management? Data-Sleek offers tailored data management solutions to ensure your patient data is secure, accessible, and optimized for better care delivery. Whether it’s enhancing interoperability, ensuring regulatory compliance, building a data warehouse, or leveraging advanced data analytics for improved patient outcomes, our experts are here to help you navigate the complexities of healthcare data management. Don’t let data challenges hold you back—partner with Data-Sleek and unlock the full potential of your healthcare data.
For a comprehensive understanding of how data management strategies can drive growth, explore our Enterprise Data Management Strategy Guide.
Contact us today for a free consultation and see how we can empower your organization to provide better, data-driven healthcare.







